Product merchandising and trade marketing are two essential strategies that brands and retailers employ to influence consumer behavior and drive sales.
While both approaches aim to enhance product visibility and demand, they differ in their focus, target audience, and execution.
Understanding these key differences is crucial for brand managers, retailers, and marketers looking to optimize their efforts and achieve their goals effectively.
Key Takeaways
- Product merchandising focuses on in-store product presentation to drive consumer purchases, while trade marketing focuses on retailer relationships and collaboration to increase product demand and sales.
- Effective product merchandising strategies include creating visually appealing displays, strategic shelf placement, and informative signage to engage consumers and drive sales.
- Successful trade marketing involves developing targeted promotional programs, joint marketing efforts, and strong partnerships with retailers and distributors.
- Cross-functional collaboration between product merchandising and trade marketing teams leads to more cohesive brand experiences and maximizes the impact of both strategies.
- Emerging trends, such as digital transformation and the growth of e-commerce, are reshaping both product merchandising and trade marketing, requiring brands to adapt their strategies accordingly.
Definitions
What is Product Merchandising?
Product merchandising encompasses the strategies and techniques used to present products that attract consumers and encourage purchases within a retail store.
It involves creating visually appealing displays, strategically placing products on shelves, and organizing items logically and engagingly.
Effective merchandising enhances the in-store experience and helps customers find what they need easily, leading to increased sales and customer satisfaction.

What is Trade Marketing?
On the other hand, trade marketing focuses on building relationships and collaborating with retailers and distributors to increase product demand and drive sales.
It involves various activities, such as trade promotions, joint marketing efforts, and retailer-specific campaigns.
The primary goal of trade marketing is to ensure that products are well-represented in stores, easily accessible to consumers, and supported by compelling promotional activities.
Key Objectives
Primary Goals of Product Merchandising
The main objectives of product merchandising align with the overall marketing goals of a brand, such as increasing brand loyalty, expanding market penetration, and driving revenue growth.
By creating attractive and informative displays, merchandising aims to capture consumer attention, educate them about product features and benefits, and ultimately persuade them to purchase.

Primary Goals of Trade Marketing
Trade marketing, in contrast, focuses on enhancing product visibility and demand through strategic partnerships with retailers and distributors.
By collaborating with trade partners, brands can secure prime shelf space, participate in retailer-specific promotions, and leverage the retailer’s customer base to expand their reach.
Trade marketing also aims to foster long-term relationships with key retailers, ensuring consistent product availability and support.
Target Audiences
Target Audience of Product Merchandising
Product merchandising directly targets consumers at the point of sale. By understanding consumer behavior, preferences, and decision-making processes, merchandisers can create displays and product arrangements that appeal to specific target audiences.
For example, a cosmetics brand may create a vibrant, interactive display to attract younger, trend-conscious consumers.
In contrast, a home appliance brand may emphasize product features and benefits to appeal to practical, value-oriented shoppers.

Target Audience of Trade Marketing
Trade marketing, on the other hand, targets retailers, distributors, and wholesalers.
By understanding these trade partners’ needs, goals, and challenges, brands can develop tailored programs and initiatives mutually benefit both parties.
For instance, a consumer goods brand may offer exclusive product launches, attractive pricing structures, or co-marketing opportunities to incentivize retailers to prioritize their products over competitors.
Strategies and Tactics
Key Strategies in Product Merchandising
Product merchandising strategies vary depending on the retail channel and product category. Some key strategies include:
- Visual Merchandising: Creating eye-catching displays, utilizing strategic shelf placement, and employing effective signage and labeling to attract consumer attention and drive sales.
- Digital Merchandising: Optimizing website design, product photography, and online product descriptions to enhance the virtual shopping experience and encourage online purchases.
- Packaging Design: Developing attractive, informative, and functional packaging that stands out on shelves and communicates key product benefits to consumers.

Key Strategies in Trade Marketing
Trade marketing strategies focus on building strong relationships with retailers and leveraging these partnerships to drive product performance. Common tactics include:
- Trade Promotions: Offering discounts, rebates, or exclusive offers to incentivize retailers to stock and promote products, ultimately driving sales and market share growth.
- Joint Marketing Efforts: Collaborating with retailers on in-store events, product demonstrations, or co-branded campaigns to enhance brand visibility and engage consumers directly.
- Trade Shows and Events: Participating in industry trade shows and events to showcase products, network with key partners, and stay informed about market trends and opportunities.
Implementation Techniques
Steps for Implementing Product Merchandising
Implementing effective product merchandising involves several key steps:
- Market Research: Conduct thorough market research to understand target audiences, competitive landscape, and industry trends, informing the development of merchandising strategies.
- Display Design: Create compelling visual displays, signage, and product arrangements that showcase products in the best possible light and align with brand identity.
- Testing and Refinement: Regularly test and refine merchandising strategies to ensure ongoing optimization and effectiveness, leveraging data-driven insights and customer feedback.

Steps for Implementing Trade Marketing
Successful trade marketing implementation begins with:
- Partner Identification: Identify and prioritize key retail partners that align with the brand’s target audience and growth objectives, focusing on mutually beneficial relationships.
- Program Development: Develop tailored programs and initiatives that address each retail partner’s needs and goals, including promotional materials and training support.
- Performance Monitoring: Consistently communicate, share data, and monitor performance to build strong, mutually beneficial relationships with trade partners and optimize marketing efforts.
Performance Metrics
Metrics for Product Merchandising
To measure the effectiveness of product merchandising efforts, brands track a range of metrics, such as:
- Sales Velocity: Monitoring the speed at which products sell through retail channels to gauge the effectiveness of merchandising strategies in driving consumer purchases.
- Conversion Rates: Analyzing the percentage of store visitors who make a purchase, indicating the ability of merchandising to persuade consumers to buy.
- Customer Engagement: Tracking metrics like dwell time and interaction rates to assess the attractiveness and persuasiveness of product displays and merchandising elements.

Metrics for Trade Marketing
Trade marketing performance is evaluated based on metrics such as:
- Retailer Adoption Rates: Measuring the percentage of targeted retailers who stock and promote the brand’s products, reflecting the success of trade marketing efforts.
- Promotional Effectiveness: Assessing the impact of trade promotions on sales lift, market share growth, and overall brand performance in retail channels.
- ROI: Monitoring the return on investment of trade marketing initiatives to ensure that resources are allocated effectively and generate the desired results.
Real-world Examples
Case Study in Product Merchandising
Coca-Cola, a global beverage giant, exemplifies excellence in product merchandising. The brand creates visually striking, branded point-of-sale displays that showcase its products in high-traffic areas of retail stores.
By leveraging eye-catching designs, strategic product placement, and effective signage, Coca-Cola consistently attracts consumer attention and drives impulse purchases.
The brand’s merchandising strategies increase sales and reinforce its brand identity and customer loyalty.
Case Study in Trade Marketing
Procter & Gamble (P&G), a leading consumer goods company, excels in trade marketing by collaborating closely with retailers to create targeted, mutually beneficial campaigns.
P&G leverages its extensive consumer insights to develop customized promotional programs that align with each retailer’s unique customer base and marketing objectives.
By partnering with retailers on exclusive product launches, joint marketing efforts, and data-driven promotions, P&G consistently drives sales growth and strengthens its trade relationships.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Product Merchandising | Trade Marketing | Examples |
|---|---|---|---|
| Focus | In-store product presentation | Retailer relationships and collaboration |
Merchandising: Eye-catching displays Trade Marketing: Joint promotions with retailers |
| Target Audience | Consumers at the point of sale | Retailers, distributors, and wholesalers |
Merchandising: Shoppers in retail stores Trade Marketing: Retail buyers and partners |
| Key Strategies | Visual displays, shelf placement, signage | Trade promotions, joint marketing, events |
Merchandising: Interactive product demos Trade Marketing: Exclusive product launches |
| Performance Metrics | Sales velocity, conversion rates, engagement | Retailer adoption, promotional ROI, market share |
Merchandising: Dwell time, impulse buys Trade Marketing: Incremental sales lift |
| Primary Goal | Drive consumer purchases | Increase product demand and sales through trade partnerships |
Merchandising: Attract shoppers, boost sales Trade Marketing: Expand retail presence, drive volume |
Budget Considerations
Cost Factors in Product Merchandising
Product merchandising budgets typically include costs associated with display materials, signage, and any special fixtures or equipment required for product presentation.
Labor costs for setting up and maintaining displays, as well as the production of promotional materials, also factor into merchandising budgets.
The scale and complexity of merchandising initiatives and the number of retail locations involved significantly influence overall costs.

Cost Factors in Trade Marketing
Trade marketing budgets encompass a wide range of expenses, including trade promotion costs, such as discounts, rebates, and incentives offered to retailers. Co-op advertising, where brands and retailers share marketing costs, is another significant expense.
Trade marketers also allocate budgets for event participation, trade show exhibits, and the production of retailer-specific promotional materials.
The depth and breadth of trade partnerships, as well as the competitiveness of the market, impact trade marketing budget requirements.
ROI Expectations and Budget Scenarios
The ROI expectations for product merchandising and trade marketing vary based on factors such as the product category, target market, and promotional strategies employed.
Generally, well-executed merchandising campaigns can generate a 10-20% increase in sales, while effective trade marketing initiatives can result in a 5-15% sales lift.
However, these figures may vary significantly depending on the specific context and budget allocated.
For example, a small business with a limited budget may focus on cost-effective merchandising tactics like strategic product placement and informative signage, aiming for a modest 5-10% sales increase.
In contrast, a large consumer goods brand with substantial trade marketing resources may invest in high-impact retailer partnerships and promotions, targeting a 15-20% sales lift and significant market share gains.
Integration Points
How Product Merchandising and Trade Marketing Work Together
While product merchandising and trade marketing have distinct focuses, they are most effective when integrated and aligned.
Trade marketing efforts help secure prime retail space and promotional support, setting the stage for effective product merchandising.
In turn, compelling merchandising drives consumer engagement and sales, enhancing the value proposition for trade partners.
Collaboration between merchandising and trade marketing teams ensures a cohesive brand experience and maximizes the impact of both strategies.

Benefits of Cross-functional Collaboration
Cross-functional collaboration between product merchandising and trade marketing teams offers several key benefits:
- Shared Insights: Exchanging insights into consumer behavior, retail trends, and competitive landscape informs the development of more targeted and effective strategies for both teams.
- Consistent Messaging: Joint planning and execution of campaigns ensure consistent messaging and visual identity across all touchpoints, reinforcing brand image and customer loyalty.
- Innovation Opportunities: Collaborating teams can brainstorm new ideas and approaches that leverage the strengths of both disciplines, driving innovation and competitive advantage.
Real-world Examples of Cross-functional Collaboration
- PepsiCo: PepsiCo’s product merchandising and trade marketing teams work closely to create impactful in-store experiences. By aligning their strategies, they develop cohesive campaigns that include eye-catching displays, targeted promotions, and retailer-specific initiatives, resulting in increased sales and stronger retailer relationships.
- L’Oréal: L’Oréal’s cross-functional approach to merchandising and trade marketing has been a key driver of its success. The company’s teams collaborate to create immersive in-store experiences, leverage data-driven insights to optimize product placement, and partner with retailers on exclusive launches and promotions, enhancing brand visibility and sales growth.
Emerging Trends
Product Merchandising vs. Trade Marketing
Digital Transformation in Product Merchandising
The rise of e-commerce and digital technologies is transforming product merchandising. Brands are increasingly investing in digital merchandising strategies, such as:
- Immersive Product Visualizations: Leveraging high-quality images, videos, and 360-degree views to provide detailed product information and simulate in-store experiences online.
- Personalized Recommendations: Utilizing customer data and AI-powered algorithms to offer personalized product suggestions and tailored merchandising experiences.
- Augmented Reality (AR) Displays: AR technology creates interactive, virtual product displays that allow customers to visualize products in real-world settings.
E-commerce Impact on Trade Marketing
The growth of e-commerce has significant implications for trade marketing. As more consumers shop online, brands must adapt their trade marketing strategies to include digital channels. This involves:
- Online Retailer Collaboration: Partnering with e-commerce platforms and online retailers to develop digital promotional campaigns and optimize product visibility in virtual retail spaces.
- Data-Driven Optimization: Leveraging data analytics and e-commerce metrics to inform trade marketing decisions and optimize product performance on digital shelves.
- Direct-to-Consumer (DTC) Strategies: Exploring DTC sales models and developing trade marketing strategies that support direct consumer engagement and loyalty.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
What is the ROI for trade marketing compared to product merchandising?
The ROI for trade marketing and merchandising varies based on product category, target market, and promotional tactics. On average, effective trade marketing can generate a 5-15% sales lift, while successful merchandising can drive a 10-20% increase in sales. However, these figures may differ significantly depending on the specific context and budget.
How does digital merchandising differ from in-store strategies?
Digital merchandising optimizes the online shopping experience through tactics like immersive product visualizations, personalized recommendations, and virtual displays. In contrast, in-store merchandising involves creating physical product displays, strategic shelf placement, and informative signage to attract and engage shoppers in retail environments.
What are some common challenges in implementing product merchandising and trade marketing strategies?
Some common challenges include:
- Aligning merchandising and trade marketing efforts with overall brand objectives
- Adapting to changing consumer preferences and retail trends
- Measuring the direct impact of specific merchandising and trade marketing initiatives on sales and ROI
- Securing buy-in and support from key stakeholders, such as retail partners and internal teams
- Allocating limited resources and budgets effectively across multiple merchandising and trade marketing activities
How can small businesses get started with product merchandising and trade marketing?
Small businesses and new brands can begin by:
- Conducting market research to understand target customers, competitors, and the retail landscape
- Developing a clear brand identity and messaging to guide merchandising and trade marketing efforts
- Focusing on cost-effective tactics like strategic product placement, informative packaging, and targeted retailer outreach
- Building relationships with local retailers and exploring co-promotional opportunities
- Leveraging digital channels and e-commerce platforms to expand reach and engage customers directly
- Continuously testing, measuring, and refining merchandising and trade marketing strategies based on performance data and customer feedback
Industry-Specific Insights
The application and effectiveness of product merchandising and trade marketing strategies can vary across different industries. Here are some brief insights:
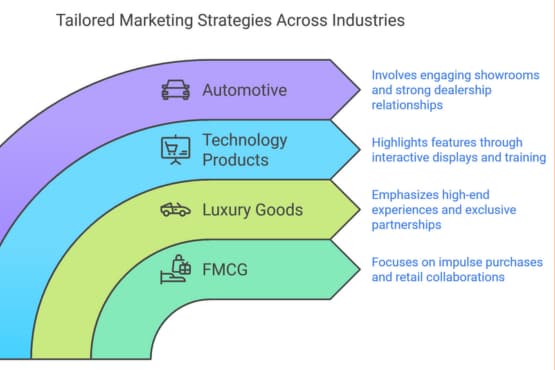
- Fast-Moving Consumer Goods (FMCG): Product merchandising is crucial in driving impulse purchases and brand loyalty in the FMCG sector. Effective packaging design, strategic shelf placement, and point-of-sale promotions are key to success. Trade marketing focuses on securing prime retail space, implementing retailer-specific promotions, and collaborating on joint marketing initiatives.
- Luxury Goods: For luxury brands, product merchandising emphasizes creating immersive, high-end retail experiences that showcase product craftsmanship and exclusivity. Trade marketing strategies often involve selective distribution partnerships, exclusive retailer collaborations, and personalized customer service to maintain brand prestige.
- Technology Products: In the tech industry, product merchandising highlights key features, benefits, and user experiences through interactive displays, product demonstrations, and informative signage. Trade marketing strategies may include retailer training programs, co-branded campaigns, and exclusive product bundles or promotions.
- Automotive: For automotive brands, product merchandising involves creating engaging showroom experiences, providing informative product displays, and offering test drives to potential customers. Trade marketing efforts focus on building strong relationships with dealership networks, implementing dealer incentive programs, and collaborating on local marketing initiatives.
Understanding each industry’s unique dynamics and customer expectations is essential for developing tailored product merchandising and trade marketing strategies that drive success.
Conclusion
Product merchandising and trade marketing are two distinct but complementary strategies that drive retail success. While product merchandising focuses on creating compelling in-store experiences to influence consumer behavior, trade marketing builds strong relationships with retailers and distributors to increase product demand and sales.
By understanding the key differences between these approaches and leveraging their unique strengths, brands can develop integrated, effective marketing strategies that engage consumers, drive sales, and foster long-term growth.
As the retail landscape continues to evolve, staying attuned to emerging trends and adapting strategies accordingly will be essential for brands to remain competitive and relevant in the ever-changing world of retail marketing.




