Marketers must navigate a multitude of strategies to drive growth and engage consumers effectively. Two prominent approaches that often come into focus are brand activation and trade marketing. While both strategies aim to boost product visibility and sales, they differ in their objectives, tactics, and target audiences.
This article will delve into the key distinctions between brand activation vs trade marketing, helping businesses make informed decisions about which approach best suits their goals.
Key Takeaways
- Brand activation focuses on direct consumer engagement, fostering emotional connections and brand loyalty.
- Trade marketing drives product availability, retailer relationships, and channel optimization.
- Use case studies and success metrics to determine the effectiveness of each approach.
- Future trends show a shift towards integrated digital and in-store activations powered by AI and personalization.
- Choosing between the two often depends on goals: use brand activation for brand-centric engagement and trade marketing for channel-driven sales growth.
Introduction
Brand activation and trade marketing are two essential strategies in the modern marketing toolkit. Brand activation focuses on creating immersive experiences that foster emotional connections between consumers and brands.
On the other hand, trade marketing concentrates on optimizing the supply chain and strengthening relationships with retailers and distributors to drive product availability and sales.
As these strategies have evolved, understanding their unique characteristics has become increasingly important for businesses looking to gain a competitive edge.
How to Choose Between Brand Activation vs Trade Marketing
When deciding between brand activation and trade marketing, consider the following factors:
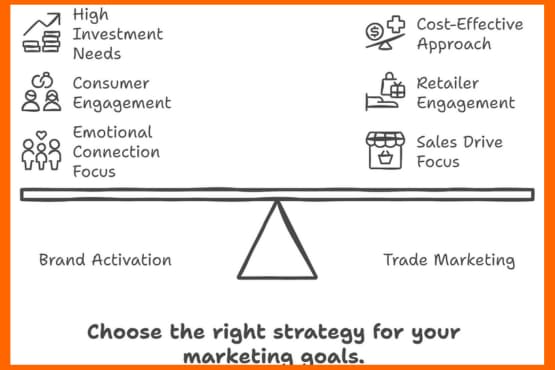
- Primary Goals: If your main objective is to create a strong emotional connection with consumers and build long-term brand loyalty, brand activation may be the better choice. However, if your focus is on driving sales through effective distribution and retailer partnerships, trade marketing should be your priority.
- Target Audience: Brand activation is ideal when you want to engage directly with end consumers, while trade marketing is more suitable when your target audience is primarily retailers, wholesalers, and distributors.
- Budget and Resources: Brand activation campaigns often require significant investments in experiential marketing, events, and digital initiatives. Trade marketing, on the other hand, may be more cost-effective, focusing on trade promotions and in-store marketing.
- Industry and Product Type: Some industries, such as FMCG and technology, have seen great success with brand activation, while others, like B2B or service-based businesses, may benefit more from trade marketing efforts.
Key Definitions and Context
Before diving into the differences between brand activation and trade marketing, let’s establish a clear understanding of each concept.
Brand Activation
Brand activation encompasses a range of marketing initiatives designed to bring brands to life through engaging, interactive experiences.
These experiences can take various forms, such as events, pop-up shops, experiential campaigns, and digital activations. The primary goal of brand activation is to create memorable interactions that leave a lasting impression on consumers, ultimately fostering brand affinity and loyalty.
One notable example of successful brand activation is Coca-Cola’s “Share a Coke” campaign. By personalizing Coca-Cola bottles with popular names and encouraging consumers to share them with friends and family, the campaign generated significant buzz and emotional connections with the brand.
The campaign resulted in a 2% increase in sales, and Coca-Cola’s Facebook community grew by 6.8% during the campaign period.

Trade Marketing
Trade marketing, on the other hand, focuses on optimizing the distribution and promotion of products through retail channels. It involves collaborating with retailers, wholesalers, and distributors to ensure optimal product placement, pricing, and promotional activities.
Trade marketing strategies aim to enhance product visibility, drive sales, and strengthen relationships with key partners in the supply chain.
A prime example of effective trade marketing is Procter & Gamble’s “First Moment of Truth” strategy.
By working closely with retailers to optimize product placement and create eye-catching displays, P&G successfully captured consumers’ attention and drove impulse purchases at the point of sale.
This strategy contributed to a 10% increase in sales for P&G’s products in the first year of implementation.
Core Objectives and Strategic Focus
While brand activation and trade marketing both contribute to a company’s overall success, their core objectives and strategic focus differ significantly.
Brand Activation Objectives
The primary objectives of brand activation are:
- Fostering emotional connections with consumers: Brand activation campaigns aim to create immersive, memorable experiences that resonate with consumers on an emotional level. By engaging the senses and evoking positive feelings, brands can establish deeper connections with their target audience.
- Building brand loyalty: Through personalized interactions and exclusive experiences, brand activation initiatives seek to cultivate a sense of belonging and loyalty among consumers. When consumers feel valued and connected to a brand, they are more likely to become long-term advocates and repeat customers.

Trade Marketing Objectives
Trade marketing, in contrast, focuses on the following objectives:
- Ensuring product availability and visibility: Trade marketing strategies aim to optimize product distribution and placement within retail outlets. By collaborating with retailers and leveraging in-store promotions, brands can ensure their products are easily accessible and visible to consumers.
- Strengthening retailer relationships: Building strong partnerships with retailers and distributors is a core objective of trade marketing. By offering attractive incentives, providing marketing support, and collaborating on joint promotions, brands can foster mutually beneficial relationships that drive sales and market share growth.
Core Tactics and Techniques
To achieve their respective objectives, brand activation and trade marketing employ distinct tactics and techniques.
Brand Activation Techniques
- Experiential marketing: Brand activation often involves creating immersive, multisensory experiences that allow consumers to interact with the brand in a memorable way. These experiences can include events, pop-up stores, product samplings, and interactive installations.
- Digital activation: In the digital age, brand activation has expanded to encompass online experiences as well. Social media campaigns, influencer partnerships, and interactive web content are all powerful tools for engaging consumers and creating viral brand moments.
Red Bull’s “Stratos” campaign is an excellent example of experiential marketing. By sponsoring Felix Baumgartner’s record-breaking skydive from the stratosphere, Red Bull created a global spectacle that showcased the brand’s values of adventure and pushing limits.
The campaign generated over 8 million live views on YouTube and resulted in a significant increase in Red Bull’s sales.

Trade Marketing Techniques
- Trade promotions: Trade marketing often involves offering special promotions and discounts to retailers to incentivize them to stock and promote a brand’s products. These promotions can include volume discounts, seasonal offers, and exclusive bundling deals.
- In-store marketing: Effective trade marketing requires optimizing the in-store experience to drive product visibility and sales. This can involve creating eye-catching displays, providing point-of-sale materials, and collaborating with retailers on in-store promotions and demonstrations.
Pepsi’s “Power of One” strategy exemplifies successful trade marketing. By leveraging data analytics and collaborating closely with retailers, Pepsi optimized its product assortment, pricing, and promotion strategies to drive sales growth across multiple channels.
This approach led to a 5% increase in net revenue and a 2% increase in market share for Pepsi.
Key Metrics and Success Measurement
Measuring the success of brand activation and trade marketing initiatives requires tracking different key performance indicators (KPIs).
Brand Activation Metrics
- Engagement metrics: Track consumer interactions across touchpoints, such as social media, event attendance, and campaign participation rates.
- Brand lift metrics: Evaluate the impact on brand perception, awareness, sentiment, and purchase intent.

Trade Marketing Metrics
- Sales performance indicators: Analyze sales volume, market share, and revenue growth across retail channels and product categories.
- Retailer satisfaction: Conduct surveys and seek feedback from retail partners to gauge the effectiveness of trade marketing efforts.
| Brand Activation | Trade Marketing |
|---|---|
| Engagement metrics Brand lift metrics Social media interactions Event attendance Campaign participation rates | Sales performance indicators Market share Revenue growth Retailer satisfaction surveys Trade promotion ROI |
Integrating Brand Activation and Trade Marketing
While brand activation and trade marketing have distinct objectives and tactics, integrating these strategies can lead to powerful synergies and amplified results.
One industry that has successfully blended brand activation and trade marketing is the fast-moving consumer goods (FMCG) sector.
Companies like Unilever and Nestlé have leveraged experiential campaigns to create buzz around new product launches while simultaneously collaborating with retailers to ensure optimal in-store placement and promotion.

In the technology industry, brands like Apple have mastered the art of integrating brand activation and trade marketing. Through immersive product launches and exclusive retail partnerships, Apple creates a seamless brand experience that drives both consumer excitement and sales performance.
Apple’s “Today at Apple” in-store events and workshops are a prime example of how the company combines experiential marketing with strategic retail partnerships to drive customer engagement and loyalty.
Audience-Specific Insights
The effectiveness of brand activation and trade marketing can vary depending on the size and nature of the business.
Here’s how different types of companies can benefit from these strategies:
Small Businesses
For small businesses with limited budgets, trade marketing can be a cost-effective way to drive sales and establish a presence in local retail outlets.
By offering attractive promotions and building relationships with local retailers, small businesses can increase their visibility and attract new customers.

Large Corporations
Large corporations can leverage their extensive resources to create high-impact brand activation campaigns that generate significant buzz and media attention.
These companies can also use their bargaining power to secure prime shelf space and exclusive promotional deals with major retailers, maximizing their trade marketing efforts.
Niche Brands
Niche brands can benefit greatly from targeted brand activation initiatives that resonate with their specific target audience.
By creating personalized experiences and collaborating with influencers in their niche, these brands can build a loyal customer base and differentiate themselves from larger competitors.
Emerging Trends and Future Insights
As the marketing landscape continues to evolve, several trends are shaping the future of brand activation and trade marketing:
- Integration of AI and Predictive Analytics: Brands are increasingly leveraging artificial intelligence and predictive analytics to optimize their trade marketing strategies. By analyzing vast amounts of sales data and consumer behavior insights, companies can make data-driven decisions about product assortment, pricing, and promotion.
- Augmented Reality in Experiential Marketing: The integration of augmented reality (AR) in brand activation campaigns is creating new opportunities for immersive and engaging consumer experiences. Brands are using AR to bring products to life, allow virtual try-ons, and gamify interactions, enhancing the impact of their experiential marketing efforts.
- Personalization in Trade Marketing: Retailers are increasingly expecting personalized trade marketing support from brands. By leveraging data on local consumer preferences and shopping behaviors, brands can tailor their trade marketing initiatives to specific regions, stores, and even individual consumers, driving higher sales and customer satisfaction.
Conclusion
Brand activation and trade marketing are two distinct yet complementary strategies that play crucial roles in driving business growth and consumer engagement.
While brand activation focuses on creating emotional connections and memorable experiences, trade marketing prioritizes product availability, retailer relationships, and sales optimization.
By understanding the key differences between these approaches and leveraging their respective strengths, businesses can develop holistic marketing strategies that resonate with consumers and drive tangible results.
Whether through immersive brand experiences or strategic retail partnerships, the power of brand activation and trade marketing lies in their ability to create meaningful connections and drive long-term success.




