Attribution modeling in marketing tracks how different marketing activities contribute to sales and conversions. For trade professionals who manage relationships between manufacturers and retailers, it’s a vital tool for understanding which marketing efforts actually drive sales.
Unlike general marketers, trade professionals deal with complex distribution networks, retail partnerships, and both online and in-store activities.
Attribution modeling helps answer critical questions: Did that in-store promotion drive sales? Was the co-branded digital campaign worth the investment? Which retail partners deliver the best results?
“Attribution modeling is the compass that guides smart budget allocation in the increasingly complex world of trade marketing,” says Jennifer Martinez, Trade Marketing Director at Kellogg’s. “Without it, you’re just guessing which half of your marketing budget works.”
What is Attribution Modeling?
Attribution modeling in marketing assigns credit to the various marketing touchpoints that lead to a customer action or purchase. For trade professionals who operate at the intersection of brands and retailers, attribution modeling takes on added complexity.
Trade marketing attribution must account for multiple layers of influence:
- Manufacturer marketing (national campaigns, brand building)
- Retail partner marketing (store promotions, loyalty programs)
- Joint marketing efforts (co-branded campaigns, retail media)
- In-store activities (displays, sampling, shelf placement)
- Digital touchpoints (websites, emails, social media)
Unlike direct-to-consumer brands, trade marketers must track how their efforts influence both retailers (B2B) and end consumers (B2C). This dual focus makes attribution particularly challenging but essential for proving marketing impact.
How Attribution Models Shape Decision-Making
The marketing attribution model you choose directly impacts how you allocate your trade marketing budget. Consider this scenario:
A customer sees a national TV ad for a new snack product, later notices it featured on a retailer’s website, receives an email about it from the store’s loyalty program, and finally purchases it in-store after seeing an end-cap display.
With first-touch attribution, the TV ad gets all the credit. With last-touch, the in-store display wins. A multi-touch model would distribute credit across all these interactions, painting a more complete picture of what really drives sales.
These different perspectives lead to vastly different budget allocations. Trade marketing teams using outdated attribution models risk funneling money into less effective channels while undervaluing critical touchpoints.
Evolution of Attribution Methods
Attribution has evolved dramatically over the past decade, particularly for trade marketers:
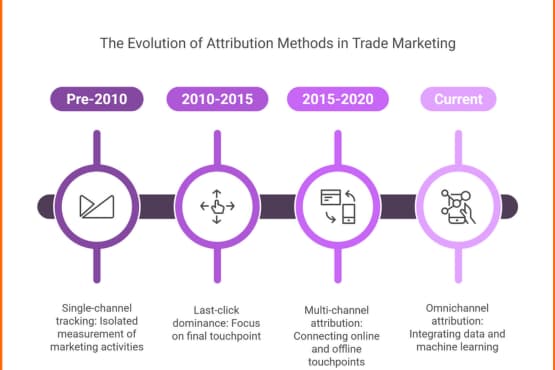
- Single-channel tracking (pre-2010): Isolated measurement of individual marketing activities with no connection between channels
- Last-click dominance (2010-2015): Heavy focus on final touchpoint, often undervaluing brand and awareness activities
- Multi-channel attribution (2015-2020): Basic models that attempted to connect online and offline touchpoints
- Omnichannel attribution (Current): Sophisticated models that integrate first-party data, machine learning, and multiple data sources
Trade marketing attribution has faced particular challenges in this evolution. While digital marketing developed robust tracking mechanisms, connecting online activities to offline retail sales remained elusive.
Recent advances in data integration, loyalty programs, and retail media networks have finally begun to bridge this gap.
2. Why Attribution Matters Today
The landscape of trade marketing has grown exponentially more complex. Gone are the days when a trade marketing manager could focus solely on in-store displays, price promotions, and relationship management with retail buyers.
The Complexity of Modern Trade Marketing
Today’s trade marketers operate across a dizzying array of channels:
- Traditional retail partnerships
- E-commerce platforms (both owned and retail partners)
- Direct-to-consumer options
- Social media marketing
- Retail media networks
- Mobile apps and loyalty programs
- Influencer partnerships
- In-store technology integrations
Each channel generates its own data, yet customers move seamlessly between them. Without proper attribution, it’s impossible to understand this complex journey and optimize marketing investments.
A 2023 survey by the Trade Marketing Association found that trade professionals who implemented advanced attribution models reported 37% faster campaign optimization cycles and 6.2x improvement in cross-channel visibility compared to those using basic models.
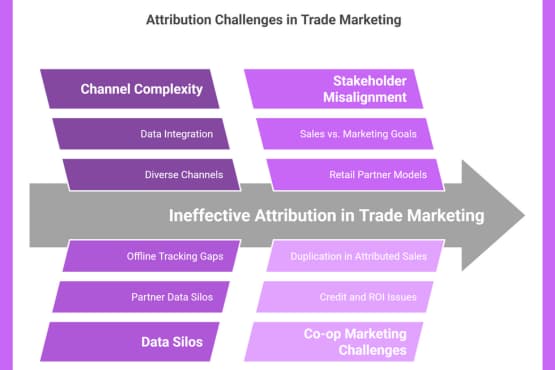
Trade-Specific Challenges
Trade marketers face unique attribution challenges that their brand marketing counterparts often avoid, especially when dealing with multiple marketing channels and touchpoints.
Partner Data Silos: Each retail partner maintains its own customer data, making it difficult to track journeys across different stores or channels.
Offline Tracking Gaps: Connecting digital marketing to in-store purchases remains difficult, with 68% of trade marketers citing it as their top attribution challenge.
Co-op Marketing Complexity: When brands and retailers jointly fund marketing initiatives, determining proper credit and ROI becomes particularly tricky.
Long Purchase Cycles: Many trade-marketed products involve consideration periods spanning weeks or months across multiple channels.
Take the example of Procter & Gamble’s trade marketing team, which struggled to measure the impact of their retail media investments across Walmart, Target, and Amazon. Their existing attribution system showed conflicting results, with each platform claiming credit for the same sales. By implementing a cross-platform attribution model, they identified a 22% duplication in attributed sales and optimized their media spend accordingly.
Aligning Stakeholders: Sales, Marketing & Retail Partners
Perhaps the most critical reason for robust attribution is stakeholder alignment. Trade marketing sits at the intersection of multiple departments and organizations:
- Internal marketing teams focused on brand building
- Sales teams measured on retailer relationships and volume
- Retail partners with their own attribution models
- Executive leadership demanding clear ROI
Without solid attribution data, these groups often work at cross-purposes. Sales might push for price promotions that erode margins while marketing advocates for brand-building activities with less immediate impact. Retail partners might take credit for sales primarily driven by brand marketing efforts.
Advanced attribution creates a shared reality based on data rather than departmental biases. It helps answer the question “what’s working?” in a way all stakeholders can accept.
3. Attribution Model Types
Trade marketers must select a marketing attribution model based on their specific business needs, data availability, and the complexity of their customer journeys. Different models serve different purposes and answer different questions.
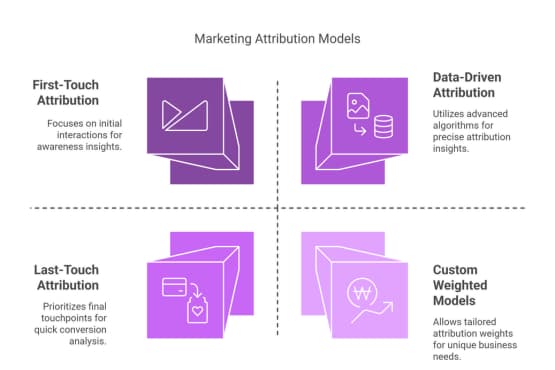
Single-Touch Models (Best for Simplicity & Speed)
Single-touch models assign 100% of the credit to one touchpoint in the customer journey. While limited in sophistication, single-touch attribution models serve specific purposes and require minimal implementation effort.
First-Touch Attribution
How it works: Gives full credit to the first interaction a customer has with your marketing.
Best for: Awareness-stage campaigns and understanding which channels bring new prospects into your funnel.
Trade marketing application: Evaluating which initial touchpoints effectively introduce new products to the market.
Limitations: Ignores all subsequent interactions that may have been crucial to the final purchase decision.
Real-world example: General Mills used first-touch attribution to evaluate a new product launch across multiple retailers. They discovered that retailer-specific digital ads were 37% more effective at driving initial awareness than their national campaign, leading them to shift budget allocation for future launches.
Last-Touch Attribution
How it works: Gives full credit to the final interaction before purchase.
Best for: Conversion-focused campaigns and understanding which channels close deals.
Trade marketing application: Identifying which in-store or online retail touchpoints drive immediate sales.
Limitations: Ignores all previous interactions that may have built awareness and consideration.
Real-world example: Unilever initially relied on last-touch attribution for their retail partnerships, which led them to heavily favor in-store promotions. After switching to a multi-touch model, they discovered their trade marketing emails actually primed customers for in-store purchases, increasing their email marketing investment by 40%.
Multi-Touch Models (Balanced Approaches)
Multi-touch models distribute credit across multiple touchpoints, providing a more nuanced view of the customer journey.
Linear Attribution
How it works: Distributes credit equally across all touchpoints in the customer journey.
Best for: Understanding the full customer journey when all interactions seem equally important.
Trade marketing application: Evaluating campaigns that span multiple retailers and channels with similar influence levels.
Limitations: Treats all touchpoints as equally important, which may not reflect reality.
Real-world example: PepsiCo’s trade marketing team used linear attribution to analyze a cross-retailer promotion, revealing that customers typically engaged with 4-6 touchpoints before purchase, spanning both manufacturer and retailer channels.
Time Decay Attribution
How it works: Gives more credit to touchpoints closer to the time of purchase, with progressively less credit to earlier interactions.
Best for: Products with short sales cycles or time-sensitive promotions.
Trade marketing application: Seasonal trade promotions or limited-time retail partnerships.
Limitations: May undervalue early awareness-building activities.
Real-world example: Nestlé applied time decay attribution to their holiday season trade marketing campaigns, finding that retail media ads delivered within 48 hours of purchase had 3.2x the impact of those delivered earlier, guiding their media buying strategy.
Position-Based Attribution (U-Shaped & W-Shaped)
How it works:
- U-Shaped: 40% credit to first touch, 40% to last touch, 20% distributed among middle interactions
- W-Shaped: 30% each to first touch, lead creation, and opportunity creation, with 10% distributed among other touchpoints
Best for: Complex B2B sales or consumer journeys with clear milestone stages.
Trade marketing application: Trade marketing campaigns with distinct awareness, consideration, and purchase phases.
Limitations: Requires clear definition of key milestones and may not fit all customer journeys.
Real-world example: Kraft Heinz implemented a W-shaped attribution model for their food service division, tracking initial awareness, sample requests, and final purchases. This model showed that culinary demonstrations were undervalued by previous attribution methods by approximately 43%.
Advanced Models (For Data-Driven Trade Marketers)
Advanced attribution models use sophisticated algorithms and machine learning to provide more accurate insights.
Data-Driven Attribution
How it works: Uses machine learning algorithms to analyze conversion patterns and assign credit based on statistical modeling.
Best for: Organizations with significant data volume and varied marketing mix.
Trade marketing application: Complex omnichannel trade marketing programs across multiple retail partners.
Limitations: Requires substantial data, technical expertise, and proper setup.
Real-world example: L’Oréal’s trade marketing division implemented a data-driven attribution model that revealed machine learning models reduced attribution errors by 39% compared to their previous rule-based systems. This insight allowed them to reallocate $1.7M in trade marketing funds to high-performing channels.
Custom Weighted Models
How it works: Allows marketers to assign custom weights to different touchpoints based on business knowledge and historical performance.
Best for: Organizations with unique business models or specific strategic objectives.
Trade marketing application: Adapting to unique trade structures like wholesale vs. direct-to-retail models.
Limitations: Requires deep business knowledge and regular recalibration.
Real-world example: Mondelēz International created a custom weighted attribution model that assigned specific values to their retail partner activities based on historical performance data. This approach improved their ability to optimize retail-specific investments, resulting in a 27% increase in trade marketing ROI.
4. Trade Marketing Benefits of Attribution
The benefits of strong attribution modeling extend far beyond simple marketing measurement. For trade professionals, attribution delivers tangible, bottom-line improvements across multiple business dimensions.
Optimizing ROI & Proving Effectiveness
In the Holiday Company Multi-Brand Optimization case study, implementing a multi-touch attribution model helped identify 37% budget waste in underperforming channels.
By redirecting these funds to top-performing channels, they achieved a 22% conversion rate increase.
Trade marketing teams face growing pressure to justify their budgets. Unlike brand marketing, which can sometimes rely on soft metrics like awareness or sentiment, trade marketing is expected to deliver measurable sales impact.
Attribution provides the evidence needed to defend and grow marketing investments.
Consider these ROI benefits from proper attribution:
- Waste reduction: Trade marketers implementing advanced attribution models report reducing marketing waste from 37% to 11% on average
- Conversion improvement: Multi-touch models show a 25% average conversion rate increase compared to single-touch models, highlighting the effectiveness of various types of attribution.
- Budget justification: Teams with solid attribution data report 70% greater success in budget approval processes
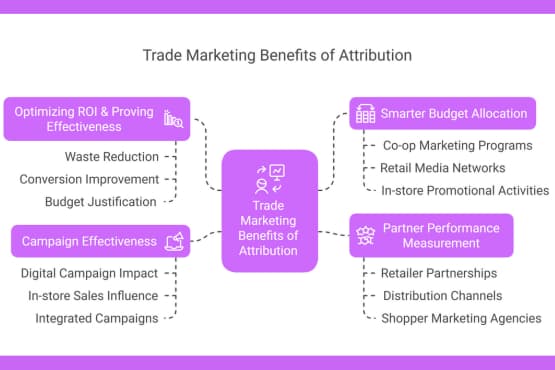
Smarter Budget Allocation Across Trade Channels
Attribution enables precise budget allocation based on actual performance rather than assumptions or historical precedent.
The Management Consulting Paid Media Revival case demonstrates this benefit clearly. By implementing causal network mapping and time-series analysis, they achieved a 75% reduction in paid media waste and sustained 6% monthly lead growth.
Most importantly, they reallocated $480,000 to high-impact channels they had previously undervalued.
For trade marketers, proper attribution helps optimize spending across:
- Co-op marketing programs with retail partners
- Retail media networks
- In-store promotional activities
- Distributor incentive programs
- Field marketing initiatives
- Digital retail support
Partner Performance Measurement
Trade marketing inherently involves multiple partners – retailers, distributors, brokers, and service providers. Attribution helps identify which partnerships deliver real value.
By analyzing attribution data across partners, trade marketers can:
- Identify which retailers provide the best return on co-marketing investments
- Compare the effectiveness of different distribution channels
- Evaluate the impact of shopper marketing agencies
- Measure the incremental sales impact of retail media networks
Campbell Soup Company used attribution modeling to evaluate their retail media partnerships across seven major retailers.
Their analysis revealed that two partners delivered 64% of total incremental sales despite receiving only 33% of the budget.
This insight led to a reallocation of retail media spending that improved overall ROI by 29%.
Campaign Effectiveness: Digital vs. Offline Attribution
Perhaps the most valuable benefit of modern attribution for trade marketers is its ability to connect digital and offline activities.
The traditional divide between digital marketing and in-store execution has created artificial silos that harm overall effectiveness.
Attribution bridges this gap by tracking the impact of digital campaigns on in-store sales and vice versa, utilizing different types of attribution models.
The D2C Ecommerce ROAS Transformation case illustrates this power. By implementing an impartial multi-touch attribution model with cross-platform analysis, they reduced marketing spend by 44% ($269,000 saved) while maintaining $6.3M in revenue, improving ROAS from 10.27 to 18.92.
Trade marketers can apply these same principles to understand how digital campaigns impact in-store sales, how in-store experiences drive online research, and how to create truly integrated campaigns that maximize effectiveness across all channels.
5. How to Implement Attribution Modeling in Trade Marketing
Implementing attribution modeling requires a systematic approach tailored to the unique needs of trade marketing.
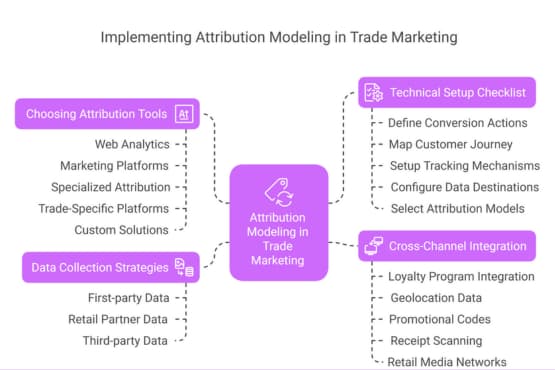
Data Collection Strategies
Effective attribution depends on collecting the right data from the right sources. For trade marketers, this means integrating data from:
First-party data sources:
- Your company website and apps
- CRM systems
- Email marketing platforms
- Customer service interactions
- Loyalty program data
Retail partner data sources are essential for understanding the impact of marketing through various types of attribution models.:
- Point-of-sale (POS) data
- Retailer loyalty programs
- Retail media platforms
- In-store promotion tracking
- Retailer website analytics
Third-party data sources:
- Media agency reporting
- Market research firms
- Payment processors
- Competitive intelligence
- Consumer panels
The key challenge is connecting these disparate data sources. Successful implementations typically involve:
- Data mapping: Creating a unified customer ID that works across platforms
- API integrations: Building direct connections between key data systems
- Data warehousing: Centralizing data from multiple sources
- Privacy compliance: Ensuring all data collection follows regulations
- Data cleaning: Standardizing formats and removing duplicates
Coca-Cola’s trade marketing team successfully implemented an integrated data collection system that combined retailer POS data, loyalty program information, and digital marketing metrics.
This integration revealed that customers exposed to both in-store displays and digital ads spent 27% more than those who saw only one or the other.
Choosing the Right Attribution Tool
Selecting the appropriate attribution tools depends on your specific trade marketing needs, technical capabilities, and budget.
Choosing the Right Attribution Tool
Selecting the appropriate attribution tools depends on your specific trade marketing needs, technical capabilities, and budget.
| Tool Type | Best For | Example Platforms | Trade Marketing Fit |
|---|---|---|---|
| Web Analytics | Digital-focused attribution with basic models | Google Analytics, Adobe Analytics | Good for digital retail support, limited for offline |
| Marketing Platforms | Multi-channel attribution within their ecosystem | Google Marketing Platform, Adobe Experience Cloud | Strong for retail media, limited for in-store |
| Specialized Attribution | Advanced cross-channel attribution | AppsFlyer, Adjust, Branch | Excellent for mobile and app-based retail |
| Trade-Specific Platforms | Retail and CPG-focused attribution | Nielsen, IRI, Blacksmith Applications | Best for connecting retail data to marketing |
| Custom Solutions | Highly specific attribution needs | Custom-built on BI platforms | Necessary for unique trade marketing models |
When selecting tools, consider these trade-specific requirements:
- Can it integrate retail point-of-sale data?
- Does it handle both online and offline touchpoints?
- Can it attribute credit across multiple retailers?
- Does it support promotional trade spending?
- Can it measure incrementality?
Heineken USA replaced their fragmented attribution tools with a unified trade marketing platform that integrated retailer data, digital marketing metrics, and distributor information.
This consolidation improved attribution accuracy by 42% and reduced reporting time by 67%.
Technical Setup Checklist
Implementing attribution requires careful technical setup. This checklist will help trade marketers navigate the process:
- Define conversion actions: What specifically counts as success? (Purchase, store visit, etc.)
- Map the customer journey: Document all potential touchpoints across channels
- Setup tracking mechanisms:
- Digital tracking codes
- Retail partner integrations
- Loyalty program connections
- Custom tracking for offline activities
- Configure data destinations: Where will attribution data be stored?
- Select attribution models: Which models align with business goals?
- Test setup: Verify accurate data collection across all touchpoints
- Establish baselines: Measure current performance as a benchmark
- Create reporting dashboards: Design for different stakeholder needs
- Train teams: Ensure everyone understands how to use attribution data
- Document governance: Who owns attribution data and decisions?
When Diageo implemented attribution modeling for their on-premise trade marketing (bars and restaurants), they faced significant technical challenges tracking offline sales.
They solved this by creating a custom venue ID system that connected promotional activities to point-of-sale data across 3,500+ venues, enabling accurate attribution of sales lift from different trade marketing tactics.
Cross-Channel Integration: Offline & Digital
Bridging the gap between online and offline channels represents the greatest technical challenge in trade marketing attribution. Successful approaches include:
Loyalty program integration: Using customer accounts to track purchases across channels. Sephora’s Beauty Insider program successfully connects online browsing to in-store purchases, allowing their trade marketing team to attribute sales accurately across channels.
Geolocation data: Tracking when customers visit stores after digital exposure. Home Depot uses this approach to measure how digital campaigns drive store visits and purchases.
Promotional codes: Using unique codes in digital marketing that customers redeem in-store. Starbucks implements this strategy to connect their app promotions to in-store redemptions.
Receipt scanning: Having customers upload purchase receipts via apps to connect to digital profiles. Ibotta has pioneered this approach, helping CPG brands track the full path from digital exposure to in-store purchase.
Retail media networks: Leveraging retailer platforms that can track users from ad exposure to purchase. Walmart Connect offers closed-loop attribution that shows which ads drive sales both online and in-store.
6. Common Challenges in Marketing Attribution
Despite its benefits, attribution modeling presents significant challenges for trade marketers. Understanding these obstacles is the first step toward overcoming them.
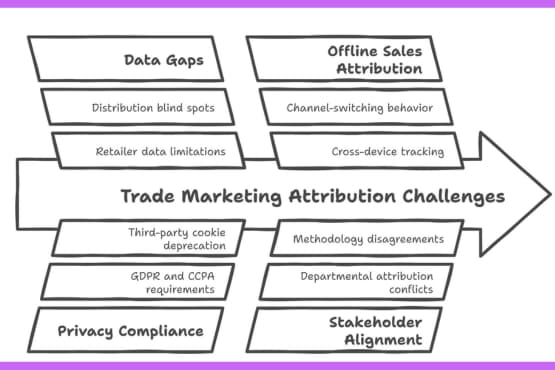
Data Gaps & Siloed Trade Information
The fragmented nature of trade marketing data creates substantial attribution barriers. Key challenges include:
Retailer data limitations: Many retailers restrict access to customer-level data or provide only aggregated sales information.
Distribution blind spots: Products passing through distributors often lose tracking connections between manufacturer and retailer.
Competitive activity impact: Competitor promotions affect sales but rarely appear in your attribution data.
Customer journey gaps: Most systems can’t track customers across different retailers or channels.
Successful trade marketers address these challenges through:
- Data partnerships: Creating mutual-benefit data sharing agreements with retail partners
- Statistical modeling: Using modeling to fill gaps where direct measurement isn’t possible
- Market research integration: Supplementing internal data with syndicated research
- Unified customer IDs: Working with retailers to implement privacy-compliant cross-channel identification
Mars Wrigley faced significant data silos across their convenience store channel, with over 150,000 independent retailers providing inconsistent sales data.
They implemented a hybrid attribution approach combining direct data from their top 25 chains with statistical modeling for smaller retailers, improving attribution coverage from 48% to 81% of total sales.
Privacy Compliance & Retailer Data Sharing
Privacy regulations have fundamentally changed attribution capabilities. Trade marketers must navigate:
GDPR and CCPA requirements: These regulations limit customer tracking across channels and websites.
Third-party cookie deprecation: Major browsers are eliminating third-party cookies, a cornerstone of traditional attribution.
Retailer data restrictions: Many retailers have become more protective of customer data, limiting what they share with trade partners.
Consent management: Tracking now requires explicit customer consent in many markets.
Leading trade marketing teams are adapting with:
- First-party data strategies built around owned touchpoints
- Privacy-enhancing technologies that measure aggregated results
- Second-party data partnerships with retailers that follow privacy regulations
- Server-side tracking that reduces reliance on cookies
- Probabilistic modeling that doesn’t require individual identification
Johnson & Johnson’s consumer health division implemented a privacy-first attribution approach after facing data sharing restrictions from key retailers.
Their solution combined anonymized loyalty card data with probabilistic modeling, maintaining 81% attribution effectiveness despite privacy limitations.
Offline Sales Attribution: The Missing Link
Connecting digital marketing to offline sales remains trade marketing’s biggest attribution challenge. Key difficulties include:
Channel-switching behavior: Customers research online but buy in-store (and vice versa).
Cross-device tracking: The same customer may use multiple devices throughout their journey.
In-store promotion measurement: Connecting displays, demos, and other in-store activities to specific sales.
Time lag challenges: The delay between marketing exposure and retail purchase complicates attribution.
Innovative trade marketers overcome these challenges with:
- Media mix modeling: Statistical approaches that identify correlations between marketing activities and sales
- Controlled experiments: Testing marketing variables in specific markets or stores vs. control groups
- Customer panels: Tracking representative customer groups across their entire shopping journey
- Integrated loyalty data: Connecting retail loyalty programs with digital marketing exposure
- Advanced location analytics: Using location data to connect digital exposure to store visits
Nestlé Waters North America struggled with attributing their digital campaigns to in-store sales until they implemented a combined approach using retailer loyalty data, location analytics, and controlled market testing.
This methodology improved their offline attribution accuracy by 62%, revealing that digital campaigns were significantly undervalued in previous models.
Stakeholder Buy-In & Alignment
Even perfect attribution models fail without organizational alignment. Common alignment challenges include:
Departmental attribution conflicts: Sales, marketing, and retail teams may each claim credit for the same results.
Methodology disagreements: Different teams often prefer different attribution approaches based on what makes them look best.
Investment justification pressure: Teams under budget pressure may resist attribution that doesn’t favor their activities.
Technical understanding gaps: Many stakeholders don’t understand attribution methodology details.
Retailer attribution differences: Your retail partners may use conflicting attribution models.
Successful trade marketing attribution requires organizational solutions:
- Executive sponsorship with clear authority to make attribution decisions
- Cross-functional attribution committees with representation from all stakeholders
- Transparent methodology documentation accessible to all teams
- Educational initiatives to build attribution literacy across the organization
- Phased implementation that gradually builds confidence in new models
Kimberly-Clark’s consumer products division created a Trade Marketing Center of Excellence that standardized attribution methodology across their organization.
By establishing clear governance and education, they reduced cross-department attribution disputes by 67% and accelerated data-based decision-making.
7. Attribution Tools & Platforms
The right attribution tools can dramatically simplify implementation and improve results. Here’s a guide to the leading options for trade marketers.

Google Attribution Suite
The Google offers several attribution tools valuable for trade marketers:
Google Analytics: Provides basic web-focused attribution models and conversion tracking.
Ads By Google: Offers campaign-specific attribution for paid search and display ads.
Google Marketing Platform: Enterprise-level attribution across multiple channels.
Best for trade marketers who: Have significant digital marketing efforts tied to retail activities and need integration with Google’s advertising ecosystem.
Limitations: Primarily focused on digital touchpoints, with limited capability for offline trade marketing activities.
Reckitt Benckiser uses Google’s attribution tools to connect their digital campaign exposure to both e-commerce purchases and in-store sales (via retailer loyalty integrations).
This approach helped them optimize their retail media spending across major retailers, improving ROAS by 27%.
Social & Retail Media Attribution Tools
Social platforms and retail media networks provide their own attribution capabilities:
Facebook Attribution: Measures impact of social advertising across the Meta ecosystem.
Amazon Marketing Cloud: Provides attribution for Amazon Advertising campaigns.
Walmart Connect: Offers closed-loop attribution for Walmart’s retail media network.
Target Roundel: Connects media exposure to purchases through Target’s loyalty program.
Best for trade marketers who: Invest heavily in retail media networks and social commerce.
Limitations: Each platform uses its own attribution methodology, creating potential conflicts and overlapping credit.
Clorox implemented a cross-platform approach to retail media attribution, using each platform’s native tools while also implementing an independent verification layer.
This dual approach identified 22% duplicated attribution claims across platforms and led to more accurate budget allocation.
Trade-Specific Attribution Software
Specialized solutions designed specifically for CPG and retail trade marketing offer unique capabilities:
Nielsen: Connects marketing activities to sales outcomes using retail measurement.
IRI: Provides attribution modeling specifically for CPG trade marketing and promotions.
Blacksmith Applications: Focuses on trade promotion attribution and optimization.
Bloomreach: Combines digital marketing attribution with commerce data.
Best for trade marketers who: Need deep retail integration and specialization in trade promotion effectiveness.
Limitations: Often require significant investment and customization to implement fully.
General Mills uses a combination of Nielsen’s attribution modeling and their own custom solutions to measure the effectiveness of their trade marketing activities, incorporating both last-click attribution and first and last models.
This approach has allowed them to attribute sales impact across both retail promotions and brand marketing activities, reducing internal disputes over marketing effectiveness.
8. FAQ Section
Which attribution model is the most accurate?
There is no universally “most accurate” attribution model – the right choice depends on your specific business objectives, sales cycle, and marketing mix. Data-driven attribution models often provide the most tailored insights because they analyze your unique conversion patterns, but they require substantial data volume to be effective; different types of attribution models can enhance this analysis.
For many trade marketers, a thoughtfully selected multi-touch model that aligns with their specific customer journey will provide the most actionable insights. The “accuracy” of any model should be judged by how well it helps you make better marketing decisions, not by an abstract standard.
When selecting a model, consider:
- How long is your typical purchase cycle?
- How many touchpoints are typically involved?
- What specific question are you trying to answer?
- What data is realistically available to you?
Why is attribution modeling so hard?
Attribution modeling presents several significant challenges:
- Incomplete visibility: It’s impossible to track every touchpoint in the customer journey, particularly offline interactions that are common in trade marketing.
- Stakeholder complexity: Different departments have conflicting attribution requirements and objectives.
- Privacy limitations: Increasing privacy regulations and the phase-out of third-party cookies restrict tracking capabilities.
- Technical integration: Connecting disparate data systems across organizational boundaries requires significant technical work.
- Multi-touch reality: Customers rarely make decisions based on a single marketing interaction, yet isolating the impact of each touchpoint is extremely difficult.
Despite these challenges, even imperfect attribution provides valuable insights compared to no attribution at all. Many trade marketers start with simple models and gradually increase sophistication as their capabilities mature.
How do I measure trade marketing effectiveness without full data?
Complete data is rarely available for trade marketing attribution, but several approaches can help maximize insights despite limitations:
Control group testing: Compare results between markets or stores with and without specific marketing activities. This isolates the impact of individual tactics without requiring complete customer journey data.
Marketing mix modeling: Use statistical analysis to correlate marketing investments with sales outcomes at an aggregate level, identifying which channels drive results without tracking individual customers.
Surveys and panels: Ask customers directly about which marketing touchpoints influenced their purchase decisions, providing qualitative insights to complement quantitative data.
Proxy metrics: When final conversion data isn’t available, use intermediate metrics that correlate with sales, such as store visits, coupon redemptions, or retailer website traffic.
Incrementality testing: Temporarily pause specific marketing activities in test markets to measure their true incremental impact compared to baseline sales.
Mondelēz International faced significant data gaps in measuring their trade marketing effectiveness across convenience stores.
By implementing a combination of controlled market tests and statistical modeling, they developed a “partial attribution” system that provided 78% of the insights of a full attribution model despite having only 40% of the ideal data inputs.
Conclusion
Attribution modeling in marketing has evolved from a nice-to-have to an essential capability for trade professionals. As the lines between digital and physical retail continue to blur, understanding which marketing activities truly drive results becomes more challenging yet more crucial than ever.
The trade marketers who master attribution will gain significant competitive advantages:
- More efficient budget allocation
- Better partnerships with retailers and distributors
- Clearer understanding of the complete customer journey
- Stronger ability to prove marketing ROI
- Greater insight into which innovations deserve investment
While implementing effective attribution isn’t easy, the case studies presented here demonstrate the substantial rewards for those who persevere. From PepsiCo to Unilever, leading consumer goods companies have achieved remarkable improvements in marketing effectiveness through strategic attribution approaches.
As privacy regulations reshape the digital landscape and AI technologies create new possibilities, trade marketing attribution will continue to evolve. The organizations that build strong attribution foundations today will be best positioned to adapt to these changes and maintain their competitive edge.
Start where you are. Even basic attribution models provide more insight than none at all. Test, learn, and gradually increase your attribution sophistication as your capabilities grow. The journey to attribution excellence is ongoing, but each step delivers greater marketing effectiveness and efficiency.
Ready to transform your trade marketing attribution? Begin by auditing your current measurement approach, identifying your biggest data gaps, and selecting the attribution model that best fits your specific business needs. The insights you gain will reshape how you plan, execute, and evaluate your trade marketing investments for years to come.